This past November, a disruptive AI tool emerged in the technology industry, known as Chat GPT, a chatbot with the seemingly miraculous ability to near-instantaneously explain complex concepts from an array of different topics and generate simple answers from scratch. There is plenty of speculation regarding its potential impact in various fields, such as the law industry: What opportunities, and subsequent challenges does disruptive AI technology introduce?

How does Chat GPT function?
Chat Generative Pretrained Transformer (Chat GPT) is a chatbot which uses a large language model trained by OpenAI and relies on a training method known as reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF).
The chatbot is specifically trained, through the use of machine learning algorithms, to analyze large sums of data and recognize language patterns and structures. Its model is designed to answer to human input in a conversational way and generate human-like text based on the context of the conversation. Its capacity to answer follow-up questions, challenge its own mistakes, and learn from past conversations makes it a truly innovative instrument in the tech realms. It can be used in various dialogue applications such as virtual assistants or customer service.
Could Chat GPT create opportunities in the legal industry?
The use of Chat GPT is flexible, and ranges from explaining coding software programs to suggesting an evening recipe for tonight’s meal based on what is left in your fridge.
AI tools are not new on the legal scene, and have long permeated the legal industry, notably through research thanks to legal research databases. Regarding Chat GPT, some consider that it could be used to draft legal documents, review contracts or even identify litigation strategies.
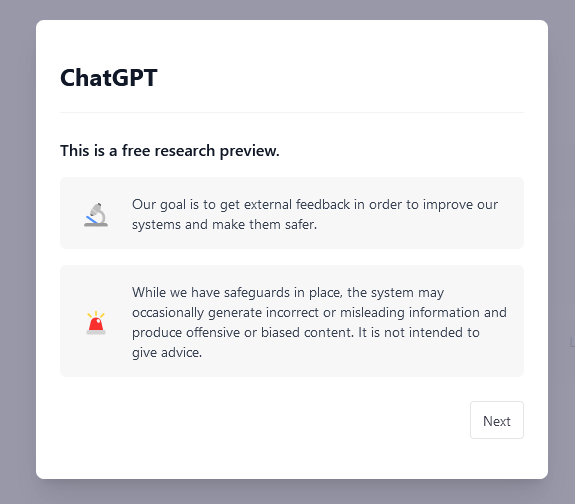
There are however certain limits that should be taken into account. OpenAI has pointed out that Chat GPT cannot provide accurate information beyond June 2021, which corresponds to its knowledge cutoff, or time stamp. Furthermore, when the task Chat GPT is given does not merely entail summarizing information, but requires critical thinking, it is prone to provide false or incomplete feedback that still remains plausible. In this respect, OpenAI warn its users that the system is not designed to give any advice.
In the legal field, error raises the question of responsibility: What happens when a wrong legal diagnosis is prescribed to the client? Lawyers are tied by a duty of diligence and competence and have their own professional civil liability in case of malpractice. The lawyer, not the chatbot it uses, bears the prejudice caused by incorrect or misleading legal advice.
What are its potential legal implications and risks?
Although Chat GPT bears significant innovative benefits, it is by no means a perfect system and is subject to limitations. Primary legal concerns range from copyright issues to cybersecurity risks.
- Copyright issues
The question of who owns the written content generated by Chat GPT is not entirely solved. The chatbot is trained on vast quantities of text from an array of different sources, so one could argue that the copyright should belong to the original owners of the data. However, the content generated by Chat GPT is usually a mix of bits and pieces of data pulled from different sources, which creates an unrecognizable pool of original content.
If we consider that OpenAI is the rightful owner of the generated content, should we need to obtain a license to use Chat GPT content for commercial purposes?
Under its Terms of use, OpenAI assigns all rights to Chat GPT content: “As between the parties and to the extent permitted by applicable law, you own all Input, and subject to your compliance with these Terms, OpenAI hereby assigns to you all its right, title and interest in and to Output”. This would mean that users can use the generated content for any purposes. There is a risk, however, that the same content be generated for other users who ask same or similar questions.
Either way, one would have to ensure that the AI is actually creating new content. In this regard, the United States Copyright Office considers that the images generated by an AI technology in response to text provided by a user are not copyrightable. The selection and arrangement of the images in a comic book is however protectable. Could the same reasoning be applied to the texts generated by Chat GPT?
- Cybersecurity setbacks
Chat GPT is able to code instantly, which could prove as a useful error and vulnerability detection tool in complex code. It thus has the potential to become a powerful cybersecurity material and could be used, for instance, to monitor chat conversations for suspicious activities.
However, if its capabilities can create a market in cyber incident management for cyber teams through simulations, Europol’s Innovation Lab warns that it can also open up opportunities for phishing attacks and impersonation attempts. Its code analysis could be used to guide hackers and fuel an already very hacker-friendly climate. Chat GPT’s backdoor capabilities must be properly understood and reigned in to limit fallout.
A focus on data privacy: how does Chat GPT interact with the GDPR?
We do not yet know what method is used by OpenAI to collect the data that Chat GPT is based on. However, we do know that such data is derived to a large extent from sources available on the Internet.
Naturally, a portion of the data gathered on the Internet may qualify as personal data. Like all processing activities, web scraping is regulated by the GDPR and, depending on national laws, may be subject to strict conditions to be legally implemented.
On March 31st, the Italian Data Protection Authority issued a ban on Chat GPT’s use and stated that “no information is provided to users and data subjects whose data are collected by Open AI; more importantly, there appears to be no legal basis underpinning the massive collection and processing of personal data in order to ‘train’ the algorithms on which the platform relies.” As such, a number of issues appear to remain unresolved regarding Chat GPT’s compliance with the GDPR.
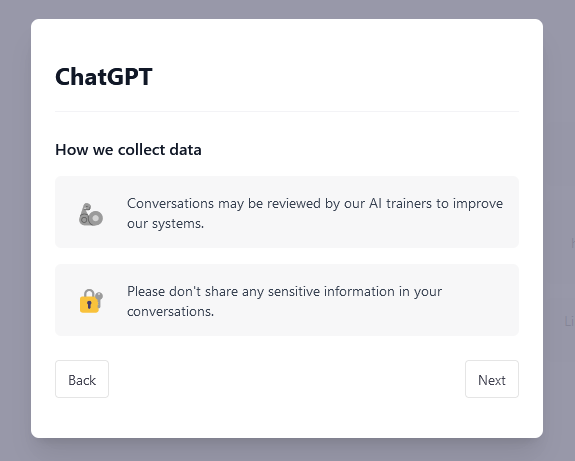
Data protection challenges also apply to interactions between Chat GPT and its users: a recent bug in an open source library led to the exposure of conversation titles to other users. It is important to note that no sensitive data should be shared in conversations, as also recommended by Open AI:
Key takeaways
Chat GPT has so far proven to be a resource friendly tool, enabling improved time and cost management. However, legal teams within any business considering its use should make sure they have appropriate safeguards in place to govern who has access to the tool, what information can be submitted, and how the output can be used.
The question raised by Chat GPT’s abilities may require further clarification by European and national courts, and Mathias Avocats will keep you informed about their response to this newly emerging artificial intelligence technology.
Mathias Avocats can help you comply with these regulations. Let’s develop your projects together and train your teams! Let’s share our expertise!
